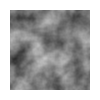
 |
Smooth 2D Noise Viewer
Perlin and Value Noise
|
 |
Smooth 2D Noise Viewer
Perlin and Value Noise
|
2D Perlin and Value noise generator. More...
#include <perlin.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| CPerlinNoise2D () | |
| Constructor. More... | |
| ~CPerlinNoise2D () | |
| Destructor. More... | |
| const float | generate (float, float, eNoise, size_t, float=0.5f, float=2.0f) const |
| Generate noise at a point. More... | |
| void | SetSeed () |
| Set seed for PRNG. More... | |
| void | RandomizeTable (eDistribution) |
| Randomize table from distribution. More... | |
| bool | DoubleTableSize () |
| Double table size. More... | |
| bool | HalveTableSize () |
| Halve table size. More... | |
| bool | DefaultTableSize () |
| Set table size to default. More... | |
| void | SetSpline (eSpline) |
| Set spline function. More... | |
| void | SetHash (eHash) |
| Set hash function. More... | |
| const size_t | GetTableSize () const |
| Get table size. More... | |
| const size_t | GetMinTableSize () const |
| Get minimum table size. More... | |
| const size_t | GetMaxTableSize () const |
| Get maximum table size. More... | |
| const size_t | GetDefTableSize () const |
| Get default table size. More... | |
| const eHash | GetHash () const |
| Get hash function type. More... | |
| const eSpline | GetSpline () const |
| Get spline function type. More... | |
| const eDistribution | GetDistribution () const |
| Get distribution type. More... | |
Private Member Functions | |
| const size_t | pair (size_t, size_t) const |
| Perlin pairing function. More... | |
| const size_t | pairstd (size_t, size_t) const |
| Std pairing function. More... | |
| const size_t | hash (size_t) const |
| Perlin hash function. More... | |
| const size_t | hashstd (size_t) const |
| std::hash function. More... | |
| const size_t | hash2 (size_t, size_t) const |
| Hash function. More... | |
| void | HashCorners (size_t, size_t, size_t[4]) const |
| Hash grid corners. More... | |
| void | RandomizeTableUniform () |
| Randomize table using uniform distribution. More... | |
| void | RandomizeTableCos () |
| Randomize table using cosine. More... | |
| void | RandomizeTableNormal () |
| Randomize table using normal distribution. More... | |
| void | RandomizeTableExp () |
| Randomize table using exponential distribution. More... | |
| void | RandomizeTableMaximal () |
| Randomize table using large magnitude values. More... | |
| void | RandomizeTableMidpoint (size_t, size_t, float) |
| Midpoint displacement. More... | |
| void | RandomizeTableMidpoint () |
| Randomize table using midpoint displacement. More... | |
| const float | spline (float) const |
| Spline curve. More... | |
| const float | z (size_t, float, float, eNoise) const |
| Apply gradients. More... | |
| const float | Lerp (float, float, float, size_t *, eNoise) const |
| Linear interpolation. More... | |
| const float | noise (float, float, eNoise) const |
| Perlin noise. More... | |
| void | RandomizePermutation () |
| Randomize permutation. More... | |
| void | Initialize () |
| Initialize. More... | |
Private Attributes | |
| eHash | m_eHash = eHash::Permutation |
| Hash function type. More... | |
| eSpline | m_eSpline = eSpline::Cubic |
| Spline function type. More... | |
| eDistribution | m_eDistribution = eDistribution::Uniform |
| Uniform distribution.. More... | |
| size_t * | m_nPerm = nullptr |
| Random permutation, used for hash function. More... | |
| float * | m_fTable = nullptr |
| Table of gradients or values. More... | |
| std::default_random_engine | m_stdRandom |
| PRNG. More... | |
| UINT | m_nSeed = 0 |
| PRNG seed. More... | |
| const size_t | m_nDefTableSize = 256 |
| Default table size. More... | |
| const size_t | m_nMinTableSize = 16 |
| Min table size. More... | |
| const size_t | m_nMaxTableSize = 1024 |
| Max table size. More... | |
| size_t | m_nSize = m_nDefTableSize |
| Table size, must be a power of 2. More... | |
| size_t | m_nMask = m_nDefTableSize - 1 |
Mask for values less than m_nSize. More... | |
This implementation of a Perlin noise generator can generate either Perlin or Value noise using gradients or values (respectively) from a table that can be filled with pseudo-random numbers from various probability distributions. There is a choice of hash functions including Perlin's original pseudo-random permutation method and various non-repeating hash functions. There is a choice of spline functions including cubic and quintic splines. The table size can be doubled or halved within hard-coded limits. The source of pseudo-randomness is std::default_random_engine
| CPerlinNoise2D::CPerlinNoise2D | ( | ) |
Set the PRNG seed and initialize.
Definition at line 42 of file perlin.cpp.
| CPerlinNoise2D::~CPerlinNoise2D | ( | ) |
Deletes the permutation and gradient/value table.
Definition at line 49 of file perlin.cpp.
| bool CPerlinNoise2D::DefaultTableSize | ( | ) |
Set table size to the default and call Initialize() to re-initialize.
Definition at line 278 of file perlin.cpp.
| bool CPerlinNoise2D::DoubleTableSize | ( | ) |
Double the size of the permutation and gradient/value tables up to a maximum of m_nMaxTableSize and call Initialize() to re-initialize.
Definition at line 245 of file perlin.cpp.
| const float CPerlinNoise2D::generate | ( | float | x, |
| float | y, | ||
| eNoise | t, | ||
| size_t | n, | ||
| float | alpha = 0.5f, |
||
| float | beta = 2.0f |
||
| ) | const |
Add multiple octaves of Perlin or Value noise to compute an effect similar to turbulence at a single point. Each successive octave has its amplitude multiplied by a value called the lacunarity and its frequency multiplied by a value called the persistence. These are usually set to 0.5 and 2.0, respectively.
| x | X-coordinate of a 2D point. |
| y | Y-coordinate of a 2D point. |
| t | Noise type. |
| n | Number of octaves. |
| alpha | Lacunarity. Defaults to 0.5f. |
| beta | Persistence. Defaults to 2.0f. |
Definition at line 548 of file perlin.cpp.
| const size_t CPerlinNoise2D::GetDefTableSize | ( | ) | const |
Reader function for the default table size.
Definition at line 602 of file perlin.cpp.
| const eDistribution CPerlinNoise2D::GetDistribution | ( | ) | const |
Reader function for the distribution type.
Definition at line 623 of file perlin.cpp.
| const eHash CPerlinNoise2D::GetHash | ( | ) | const |
Reader function for the hash function type.
Definition at line 609 of file perlin.cpp.
| const size_t CPerlinNoise2D::GetMaxTableSize | ( | ) | const |
Reader function for the maximum table size.
Definition at line 595 of file perlin.cpp.
| const size_t CPerlinNoise2D::GetMinTableSize | ( | ) | const |
Reader function for the minimum table size.
Definition at line 588 of file perlin.cpp.
| const eSpline CPerlinNoise2D::GetSpline | ( | ) | const |
Reader function for the spline function type.
Definition at line 616 of file perlin.cpp.
| const size_t CPerlinNoise2D::GetTableSize | ( | ) | const |
Reader function for the table size.
Definition at line 581 of file perlin.cpp.
| bool CPerlinNoise2D::HalveTableSize | ( | ) |
Halve the size of the permutation and gradient/value tables down to a minimum of m_nMinTableSize and call Initialize() to re-initialize.
Definition at line 262 of file perlin.cpp.
|
inlineprivate |
Perlin's hash function, which uses a random permutation. Note that this means that it repeats with a period of m_nSize.
| x | A number. |
m_nSize - 1]. Definition at line 367 of file perlin.cpp.
|
inlineprivate |
A 2D linear congruential hash function. For fixed primes \(p_0, p_1, p_2\) and parameters \(x, y\), this function returns \((p_0x + p_1y) \bmod p_2 \) right-shifted by 8 bits and masked with m_nMask.
| x | A number. |
| y | A number. |
m_nSize - 1]. Definition at line 389 of file perlin.cpp.
|
private |
Get hash values at grid corners (at whole number coordinates).
| x | X-coordinate. |
| y | Y-coordinate. |
| c | [OUT] Array of four hash values for corners in row-major order. |
Definition at line 404 of file perlin.cpp.
|
inlineprivate |
A hash function using std::hash. Note: The C++ Standard does not require that std::hash be a good hash function, but we'll assume that it is. Most implementations are.
| x | A number. |
m_nSize - 1]. Definition at line 377 of file perlin.cpp.
|
private |
Initialize the generator. Assumes that m_nSize has set initialized to the table size, which must be a power of two. Create and initialize the permutation and gradient/value tables. Initialize the bit mask.
Definition at line 58 of file perlin.cpp.
|
private |
Linear interpolation of gradients or heights (depending on whether we're generating Perlin or Value noise) along the X-axis.
| sX | Smoothed fractional part of X-coordinate. |
| fX | Fractional part of X-coordinate (ignored in Value noise). |
| fY | Fractional part of Y-coordinate (ignored in Value noise). |
| c | Array of two gradients at grid points along X-axis. |
| t | Noise type. |
Definition at line 466 of file perlin.cpp.
|
private |
Compute a single octave of Perlin or Value noise at a 2D point.
| x | X-coordinate of point. |
| y | Y-coordinate of point. |
| t | Noise type. |
Definition at line 506 of file perlin.cpp.
|
inlineprivate |
Perlin's pairing function, which combines two unsigned integers into one.
| x | First unsigned integer. |
| y | Second unsigned integer. |
Definition at line 346 of file perlin.cpp.
|
inlineprivate |
Alternate version of Perlin's pairing function. Note: This function depends on the implementation of std::hash. The C++ Standard does not require that it be a good hash function, but we'll assume that it is. Most implementations are.
| x | First number. |
| y | Second number. |
Definition at line 358 of file perlin.cpp.
|
private |
Use the standard algorithm to set the permutation in m_nPerm to a pseudo-random permutation with each permutation equally likely . The source of randomness is std::default_random_engine with std::uniform_int_distribution. This function should be called during initialization and when the table size changes. The pseudo-random number generator is re-seeded from m_nSeed before the permutation is generated. This means that the permutation used for each table size remains the same until m_nSeed is changed.
Definition at line 86 of file perlin.cpp.
| void CPerlinNoise2D::RandomizeTable | ( | eDistribution | d | ) |
Set m_fTable to pseudo-random values in \([-1, 1]\) according to some probability distribution. The pseudo-random number generator is re-seeded from m_nSeed before the table is generated. This means that the table contents for each table size remains the same until m_nSeed is changed.
| d | Probability distribution enumerated type. |
Definition at line 227 of file perlin.cpp.
|
private |
Fill the gradient/value table m_fTable using a cosine distribution. The source of randomness is std::default_random_engine with std::uniform_real_distribution<float>(0.0f, 1.0f). It simply multiplies the each pseudo-random number by \(pi\) and enters the cosine of the result into the table.
Definition at line 194 of file perlin.cpp.
|
private |
Fill the gradient/value table m_fTable using an exponential distribution. The source of randomness is std::default_random_engine with std::exponential_distribution<float>(8.0f). It fills half of the table with negative gradients and half with positive gradients.
Definition at line 208 of file perlin.cpp.
|
private |
Fill the gradient/value table m_fTable with large magnitude entries, that is, either -1 ot +1, using a uniform distribution. The source of randomness is std::default_random_engine with std::uniform_real_distribution<float>(-1.0f, 1.0f).
Definition at line 166 of file perlin.cpp.
|
private |
Fill the gradient/value table m_fTable using midpoint displacement. This function fills in the first and last entries then calls the recursive RandomizeTableMidpoint(size_t, size_t, float) to fill in the rest.
Definition at line 141 of file perlin.cpp.
|
private |
Initialize a chunk of the gradient/value table m_fTable using midpoint displacement. Given \(\mathsf{i}\) and \(\mathsf{j}\) such that \(\mathsf{j} > \mathsf{i}+1\) and \(0 \leq \mathsf{i}, \mathsf{j} \leq\) m_nSize, where \(\mathsf{j} - \mathsf{i}\) is a power of 2, this function assumes that m_fTable \([\mathsf{i}]\) and m_fTable \([\mathsf{j}]\) have been set, and fills in the entries m_fTable \([\mathsf{i} + 1]\) through m_fTable \([\mathsf{j}-1]\) recursively using midpoint displacement. That is, it sets the middle entry to the average of the first and last entry offset by a pseudo-random value in \([-1,1]\) times a value called the lacunarity. The function then halves the lacunarity and calls itself recursively on the top and bottom halves of the table chunk. The source of randomness is std::default_random_engine with std::uniform_real_distribution<float>(-1.0f, 1.0f).
| i | Lower index. |
| j | Upper index. |
| alpha | Lacunarity. |
Definition at line 116 of file perlin.cpp.
|
private |
Fill the gradient/value table m_fTable using a normal distribution. The source of randomness is std::default_random_engine with std::normal_distribution<float>(500.0f, 200.0f).
Definition at line 179 of file perlin.cpp.
|
private |
Fill the gradient/value table m_fTable using a uniform distribution. The source of randomness is std::default_random_engine with std::uniform_real_distribution<float>(-1.0f, 1.0f).
Definition at line 152 of file perlin.cpp.
| void CPerlinNoise2D::SetHash | ( | eHash | d | ) |
Set the hash function type.
| d | Hash function enumerated type. |
Definition at line 309 of file perlin.cpp.
| void CPerlinNoise2D::SetSeed | ( | ) |
Set the pseudo-random number generator seed to timeGetTime(), the number of milliseconds since Windows last rebooted. This should be sufficiently unpredictable to make a good seed.
Definition at line 295 of file perlin.cpp.
| void CPerlinNoise2D::SetSpline | ( | eSpline | d | ) |
Set the spline function type.
| d | Spline function enumerated type. |
Definition at line 302 of file perlin.cpp.
|
inlineprivate |
Compute a spline function. Depending on the value of m_eSpline this will be either identity function, a cubic spline, or a quintic spline.
| x | A float in the range \([-1, 1]\). |
Definition at line 325 of file perlin.cpp.
|
inlineprivate |
For Perlin noise, multiply hashed gradient from m_fTable by coordinates. Use the hash value parameter to index into the gradient table for the X gradient and rehash it for the index of the Y gradient. Add these gradients multiplied by the fractional values of the position (that is, return \(z = x \frac{dz}{dx} + y\frac{dz}{dy}\)). For Value noise, just read the \(z\) value directly from the table.
| h | Hash value for gradient table index. |
| x | X-coordinate of point in the range \([-1, 1]\). |
| y | Y-coordinate of point in the range \([-1, 1]\). |
| t | Noise type. |
Definition at line 435 of file perlin.cpp.
|
private |
|
private |
|
private |